# Time-Series Sensor Forecasting (TSF) AI Blueprint - deprecated from 11/2024
# Inference
Sensor forecasting involves training models on historical, time-series sensor data and using the trained models to predict future values coming from the same sensor types. Using these predictions, companies can set thresholds for normal device operations to predict whether future sensor values exceed the set thresholds.
# Purpose
Use this inference blueprint to immediately forecast sensor values in a dataset. To use this pretrained sensor-forecaster model, create a ready-to-use API-endpoint that can be quickly integrated with your data and application.
This inference blueprint’s model was trained using Skoltech Anomaly Benchmark (SKAB) datasets. To use custom data according to your specific business, run one of this counterpart’s training blueprints, currently InfluxDB TSF Train and S3 TSF Train, which trains the model and establishes an endpoint based on the newly trained model.
# Instructions
NOTE
The minimum resource recommendations to run this blueprint are 3.5 CPU and 8 GB RAM.
Complete the following steps to deploy a time-series sensor-forecaster API endpoint:
- Click the Use Blueprint button.
- In the dialog, select the relevant compute to deploy the API endpoint and click the Start button.
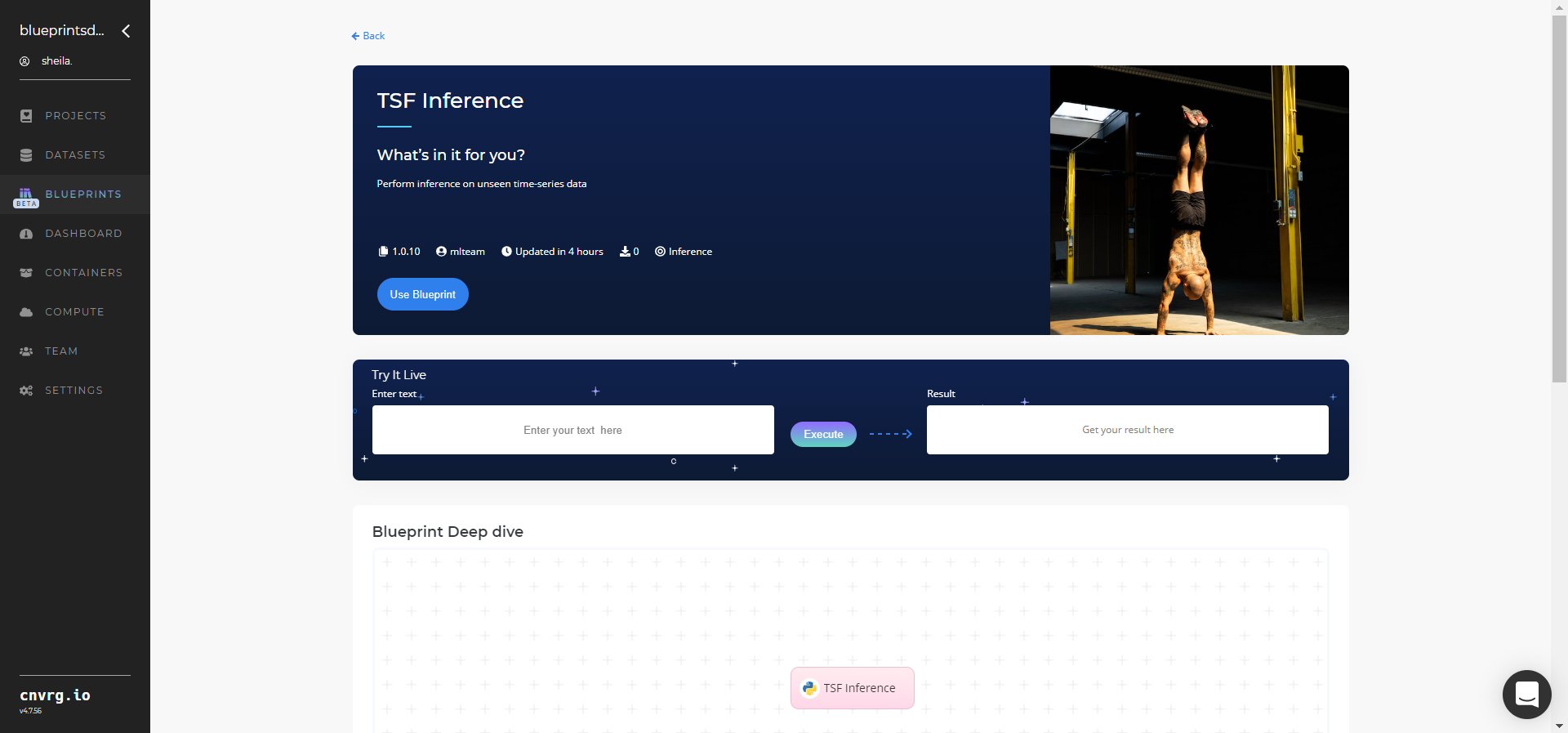
- The cnvrg software redirects to your endpoint. Complete one or both of the following options:
- Use the Try it Live section with any data to check the model.
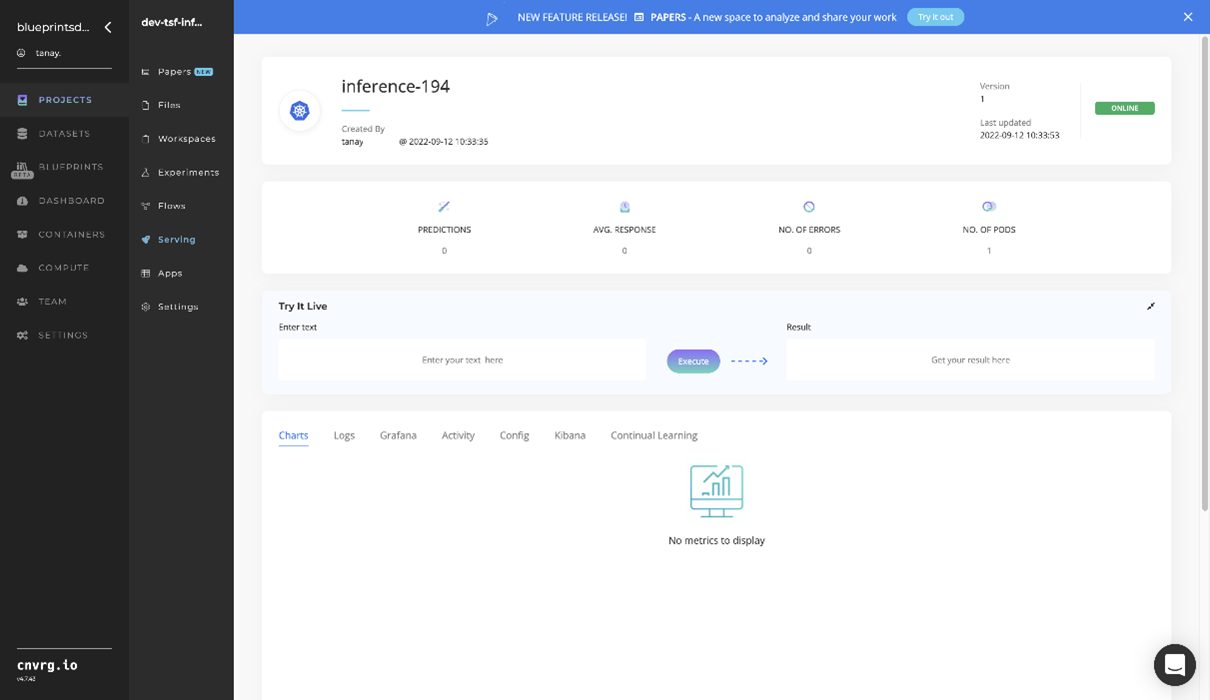
- Use the bottom integration panel to integrate your API with your code by copying in the code snippet.
- Use the Try it Live section with any data to check the model.
An API endpoint that predicts future sensor values has now been deployed. For information on this blueprint's software version and release details, click here.
# Related Blueprints
The following blueprints are related to this inference blueprint:
# Training
Sensor forecasting involves training models on historical, time-series sensor data and using the trained models to predict future values coming from the same sensor types. Using these predictions, companies can set thresholds for normal device operations to predict whether future sensor values exceed the set thresholds.
# Overview
The following diagram provides an overview of this blueprint’s inputs and outputs.
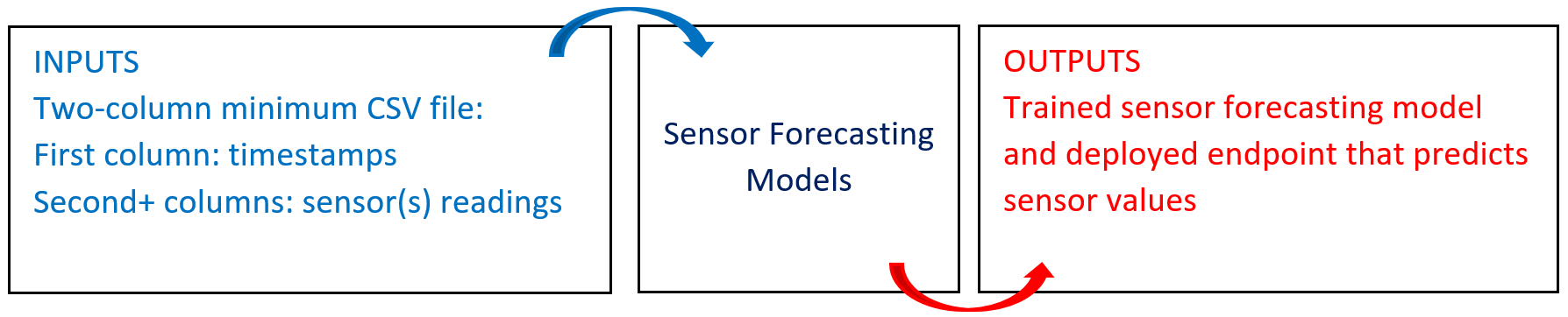
# Purpose
Use this training blueprint with various connectors, currently InfluxDB TSF Train and S3 TSF Train, to train forecasting models on historical, multiple-sensor, time-series data so future data points coming from the same sensor types can be predicted. This blueprint requires a two-column minimum CSV file of input data:
- Columns - first column: a timestamp; second and subsequent columns: sensor value readings
- Rows - Each row of data represents a time-stamped reading from the sensor(s)
To run this sensor-value forecasting blueprint, provide the input data in CSV format, which the blueprint uses to train multiple algorithms. The best performing algorithms are selected and deployed as an API endpoint. Then, users can call this API to test new data points and view responses and whether they exceed thresholds.
# Deep Dive
The following flow diagram, with different data and batch connector options, illustrates this blueprint’s pipeline:
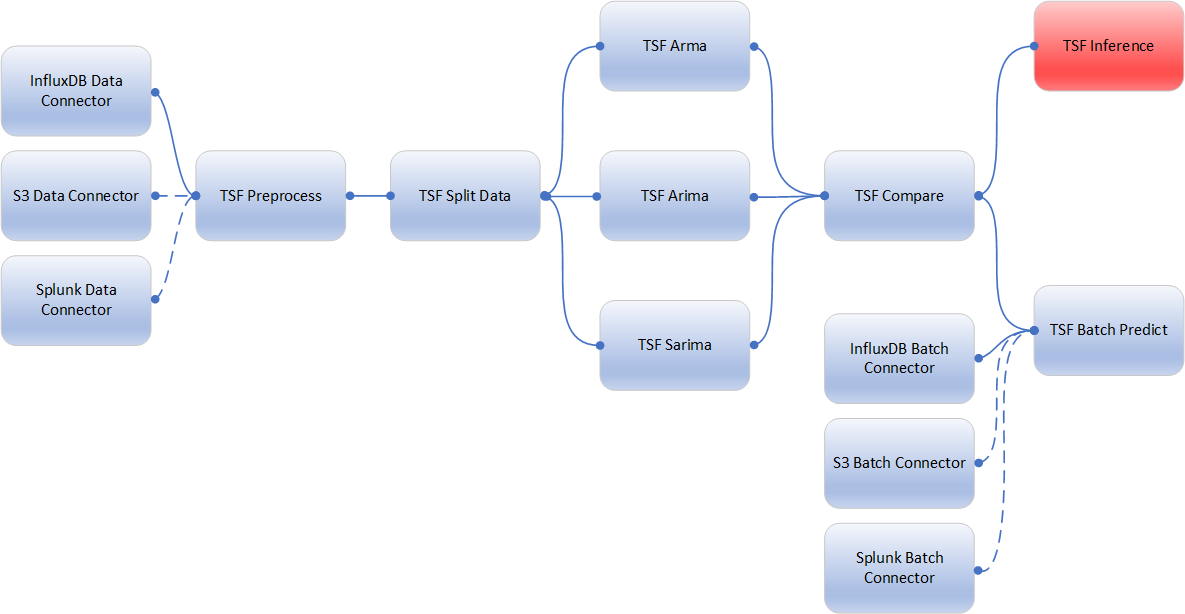 This blueprint can be used with the desired data and batch connectors. The above diagram illustrates the data and batch connectors required to access the InfluxDB online data storage platform.
This blueprint can be used with the desired data and batch connectors. The above diagram illustrates the data and batch connectors required to access the InfluxDB online data storage platform.
NOTE
This blueprint currently runs with either the InfluxDB Connector or the S3 Connector. Its use with the Splunk Connector will be coming soon.
# Flow
The following list provides a high-level flow of this blueprint’s run:
- The user obtains data in CSV format using a connector library such as S3, InfluxDB, or in the future, Splunk. In this use case, the InfluxDB Connector from the InfluxDB library is being used.
- The TSF-Preprocess task allows the user to filter the dataset by columns of interest, perform data imputation on missing data, and store the preprocessed file and imputer as output artifacts.
- The TSF-Split task splits the preprocessed dataset into train and test sets. The user selects the data percentage going in the
train.csvfile, with the remaining data being stored intest.csv. - The blueprint then trains in parallel three time-series forecasting models (ARMA, ARIMA, SARIMA) on the
train.csvandtest.csvfiles. - The TSF-Compare task selects the best-performing model based on the root-mean-square error (RMSE) metric.
- The user uses the TSF-Inference task to make a prediction dynamically with new data using the newly trained model.
- The user provides a size and uses the TSF-Batch Predict task to make predictions with new data using the newly trained model.
# Arguments/Artifacts
For more information on this blueprint’s tasks, its inputs, and outputs, click here.
# Inputs
Historical input data coming from multiple sensors should meet the following criteria:
- The input data measurements can be high-frequency (millisecond time scale) or low-frequency (second time scale) data, depending on your company requirements.
- The historical input data is preprocessed to address and adjust missing values in a manner appropriate and relevant to time-series sensor data readings. Users can select (based on their expertise) if they want to drop rows with any missing values or attempt to impute missing values. The blueprint selects an imputer (mean, median, or KNN) to handle missing sensor data.
- The preprocessing step produces a flat table with timestamp and columns of numeric values without missing data points.
# Outputs
- The blueprint generates an output file that contains a copy of the original training data and a column for each sensor, showing the model predictions for existing values, future model predictions, and upper and lower bounds (95% confidence) for the model predictions call to the endpoint.
- The blueprint generates one chart per column of sensors with forecasted data overlaid on actual data, as well as confidence intervals. The x-axis displays the timestamp and the y-axis displays the sensor values.
- This blueprint also outputs standard RMSE time-series metrics to assess model performance.
# Instructions
NOTE
The minimum resource recommendations to run this blueprint are 3.5 CPU and 8 GB RAM.
NOTE
This blueprint involves running multiple experiments to determine the best algorithm and version for API deployment use based on a custom dataset. Running this blueprint may exhaust your free resources if you are using the community version.
Complete the following steps to train a sensor-forecaster model:
Click the Use Blueprint button.
Click the (Connector Name) Data Connector to display its dialog; configure it based on the specific connector.
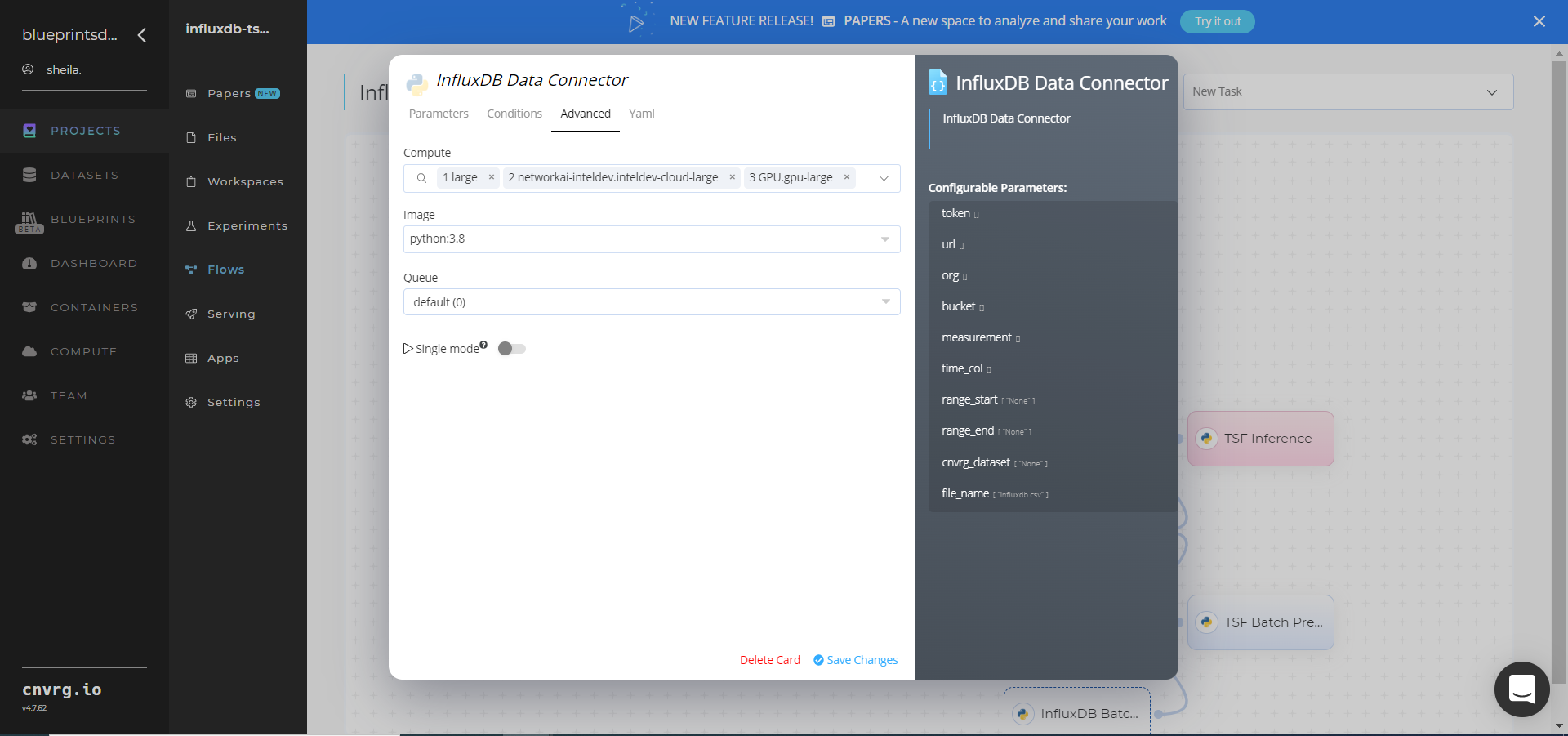
- Within the InfluxDB Data Connector > Parameters tab, provide the following Key-Value pair information:
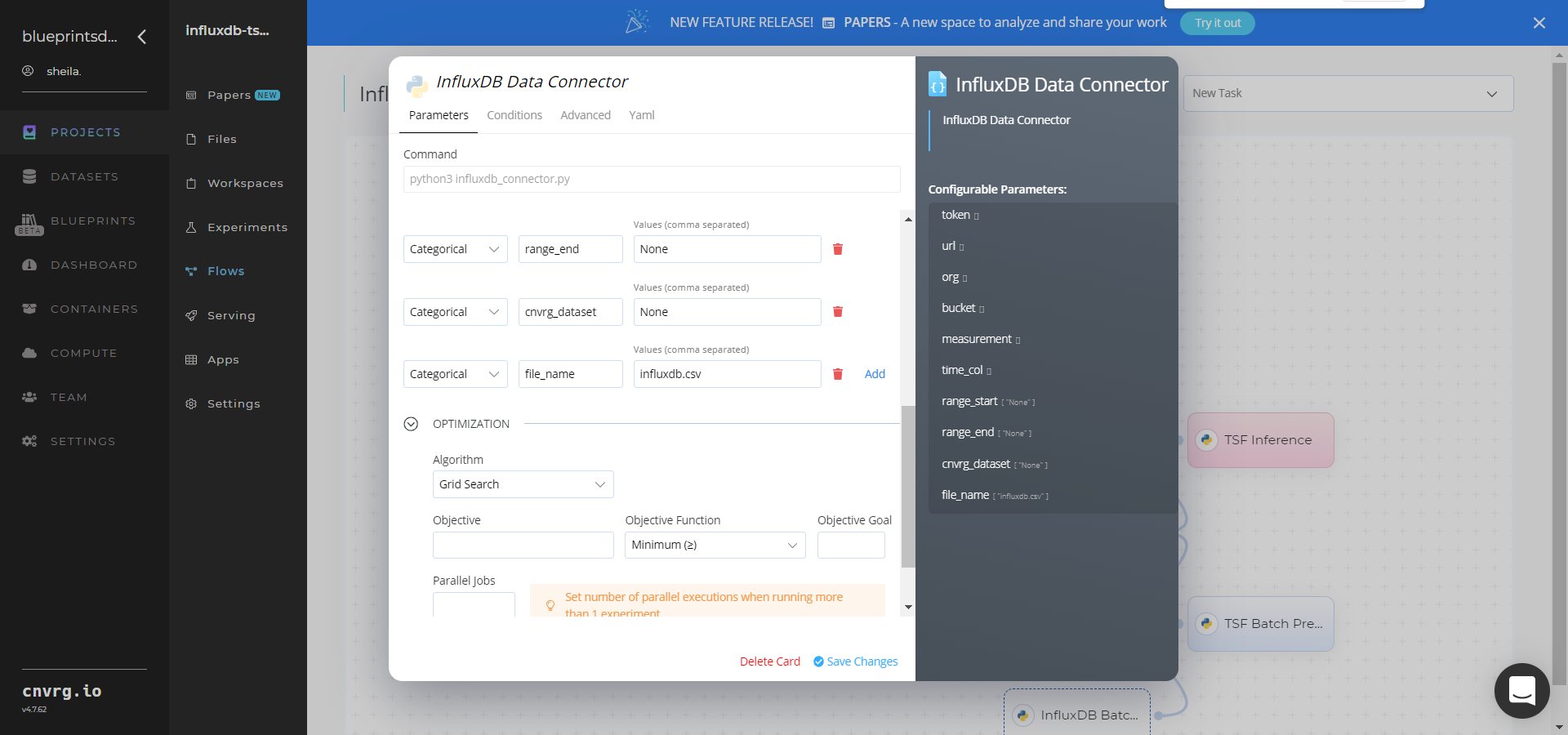
- Key:
token– Value: provide the InfluxDB API token - Key:
url– Value: provide the InfluxDB URL - Key:
org– Value: provide the organization email - Key:
bucket– Value: provide the bucket name - Key:
measurement– Value: provide the name of the measurement to pull data from - Key:
time_col– Value: provide the name of the time column - Key:
range_start– Value: specify the start date for pulling time-series data from InfluxDB - Key:
range_end– Value: specify the end date for pulling time-series data from InfluxDB - Key:
cnvrg_dataset– Value: set to store the time-series data as a cnvrg dataset - Key:
file_name– Value: name the output CSV file
- Key:
- Click the InfluxDB Data Connector > Advanced tab to change resources to run the blueprint, as required.
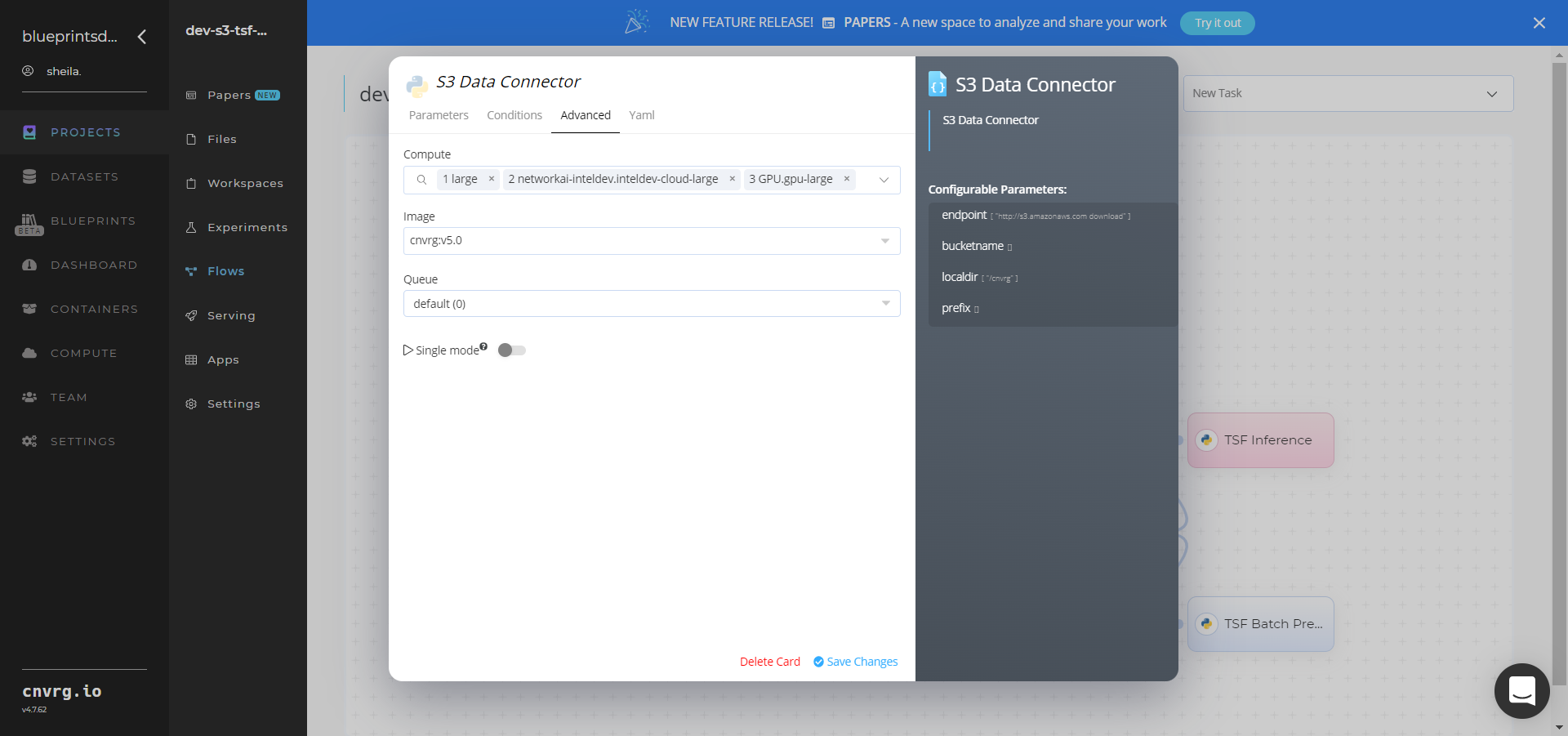
- Within the S3 Data Connector > Parameters tab, provide the following Key-Value pair information:
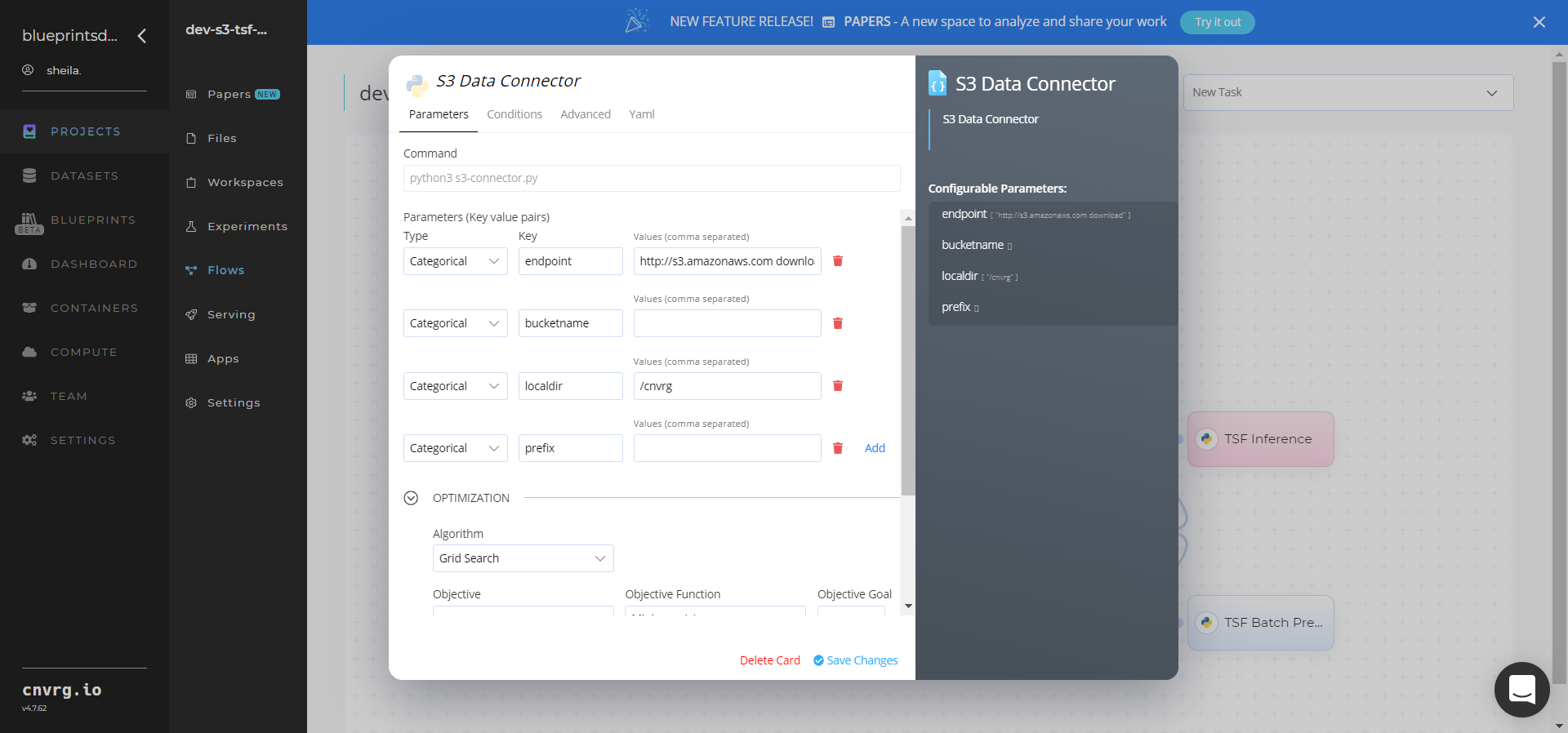
- Key:
bucketname– Value: provide the bucket name - Key:
prefix− Value: provide the main path to the data folder
- Key:
- Click the S3 Data Connector > Advanced tab to change resources to run the blueprint, as required.
- Within the InfluxDB Data Connector > Parameters tab, provide the following Key-Value pair information:
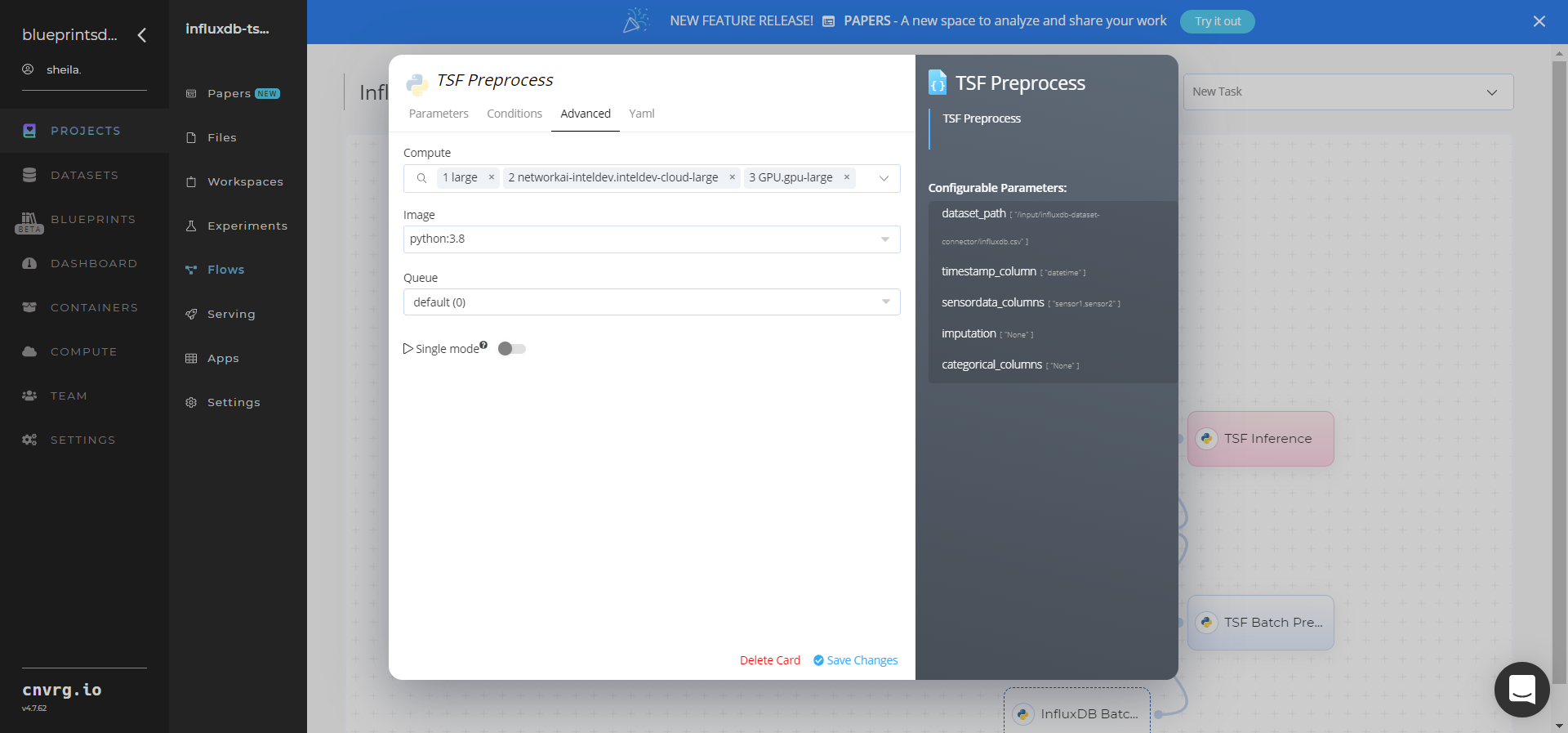
Click the TSF Preprocessing task to display its dialog.
Within the Parameters tab, provide the following Key-Value pair information:
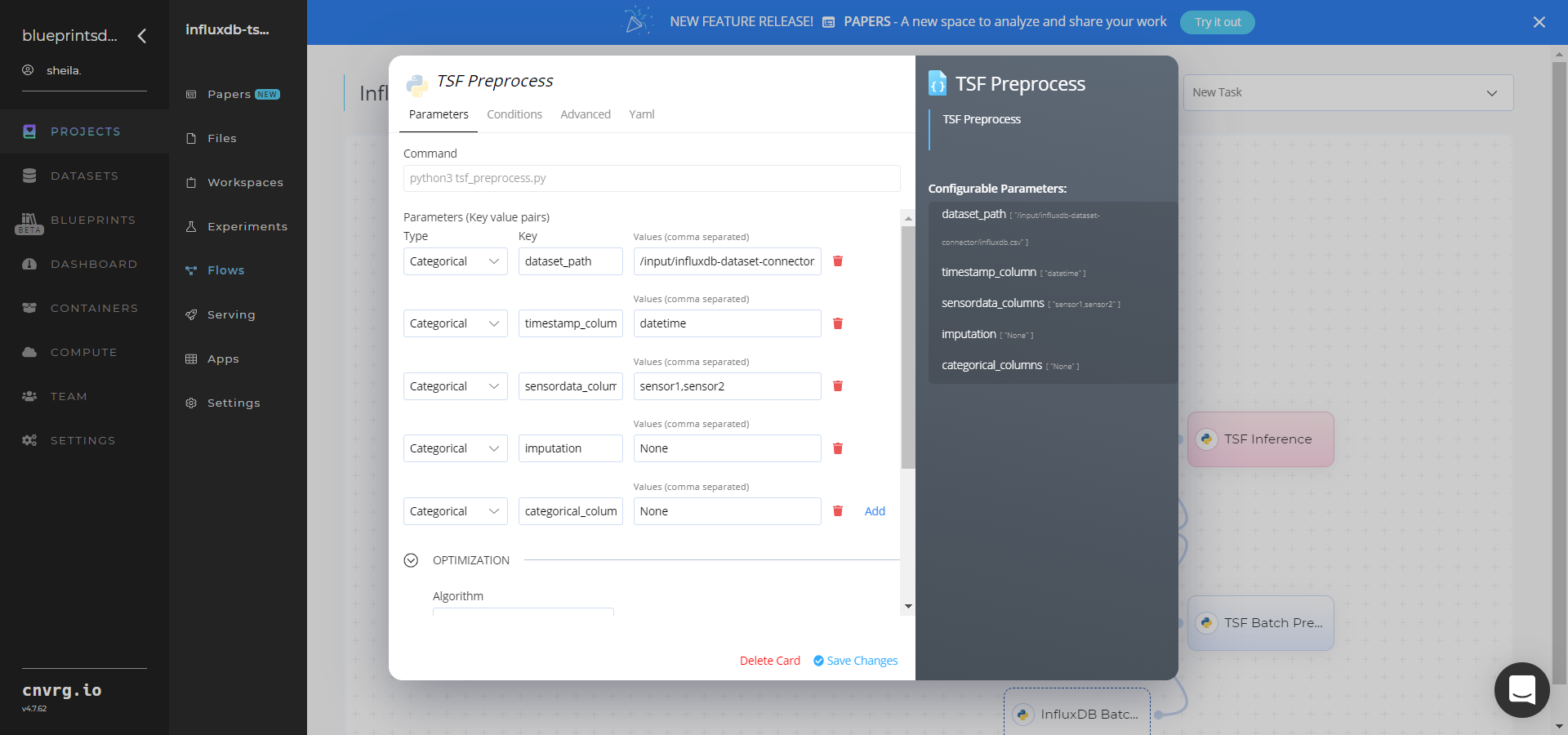
- Key:
dataset_path– Value: provide the path to the input CSV-formatted dataset including the connector location prefix - Key:
timestamp_column– Value: provide the column name for one with timestamp/date/time values - Key:
sensordata_columns– Value: provide comma-separated names for columns with sensor data values - Key:
imputation– Value: provide the comma-separated data imputation techniques (1-mean, 2-median, 3-KNN) for all sensor data columns; default:None - Key:
categorical_columns– Value: provide comma-separated names for columns with categorical values; default:None
NOTE
You can use the prebuilt example data paths provided.
- Key:
Click the Advanced tab to change resources to run the blueprint, as required.
Click the TSF Split Data task to display its dialog.
Within the Parameters tab, provide the following Key-Value pair information:
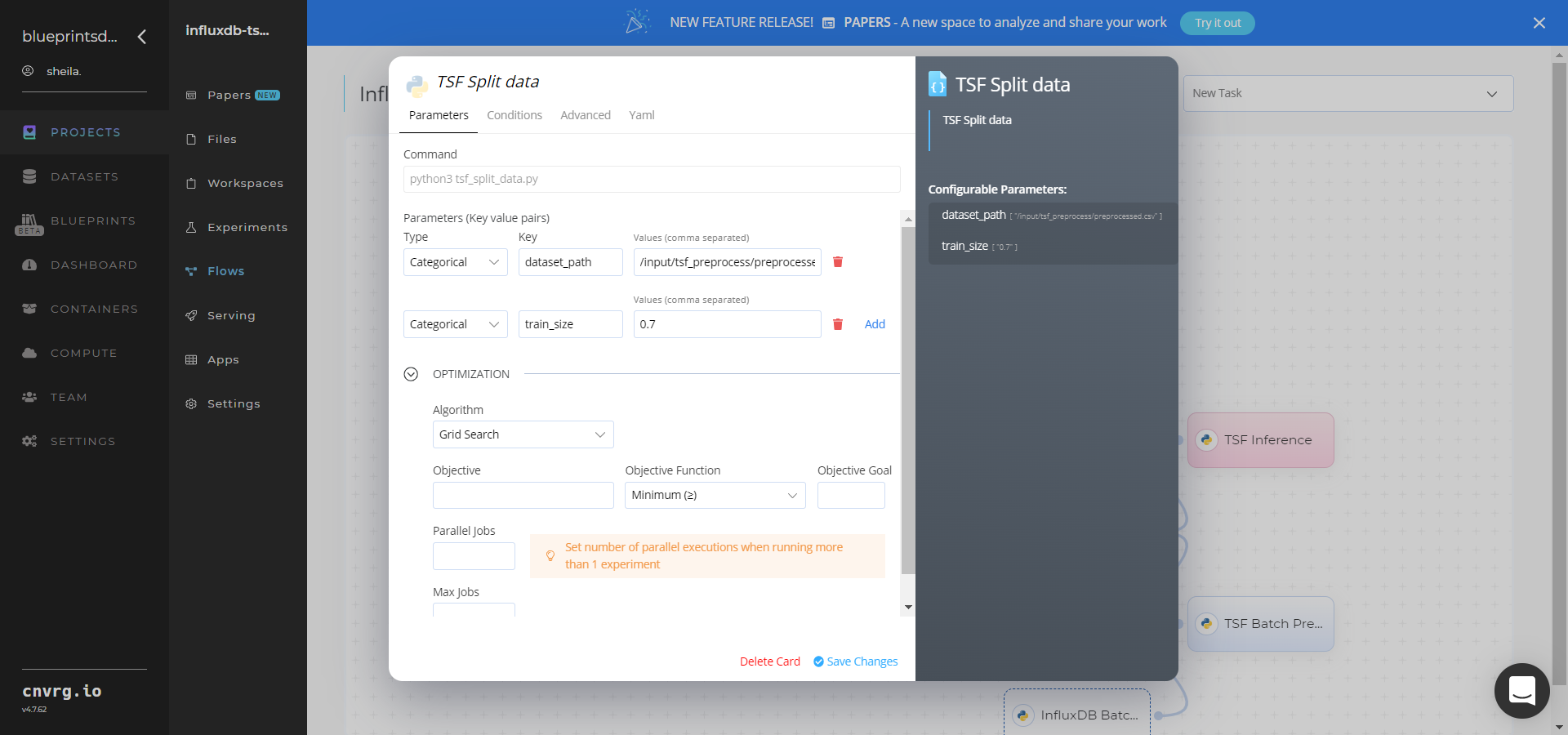
- Key:
dataset_path– Value: provide the path to thepreprocessed.csvdataset including thetsf_preprocessprefix - Key:
train_size– Value: set the size of the validation set as a number between 0.0 and 1.0
NOTE
You can use the prebuilt example data paths provided.
- Key:
Click the Advanced tab to change resources to run the blueprint, as required.
Click the (Connector Name) Batch Connector task to display its dialog and configure it based on the specific connector.
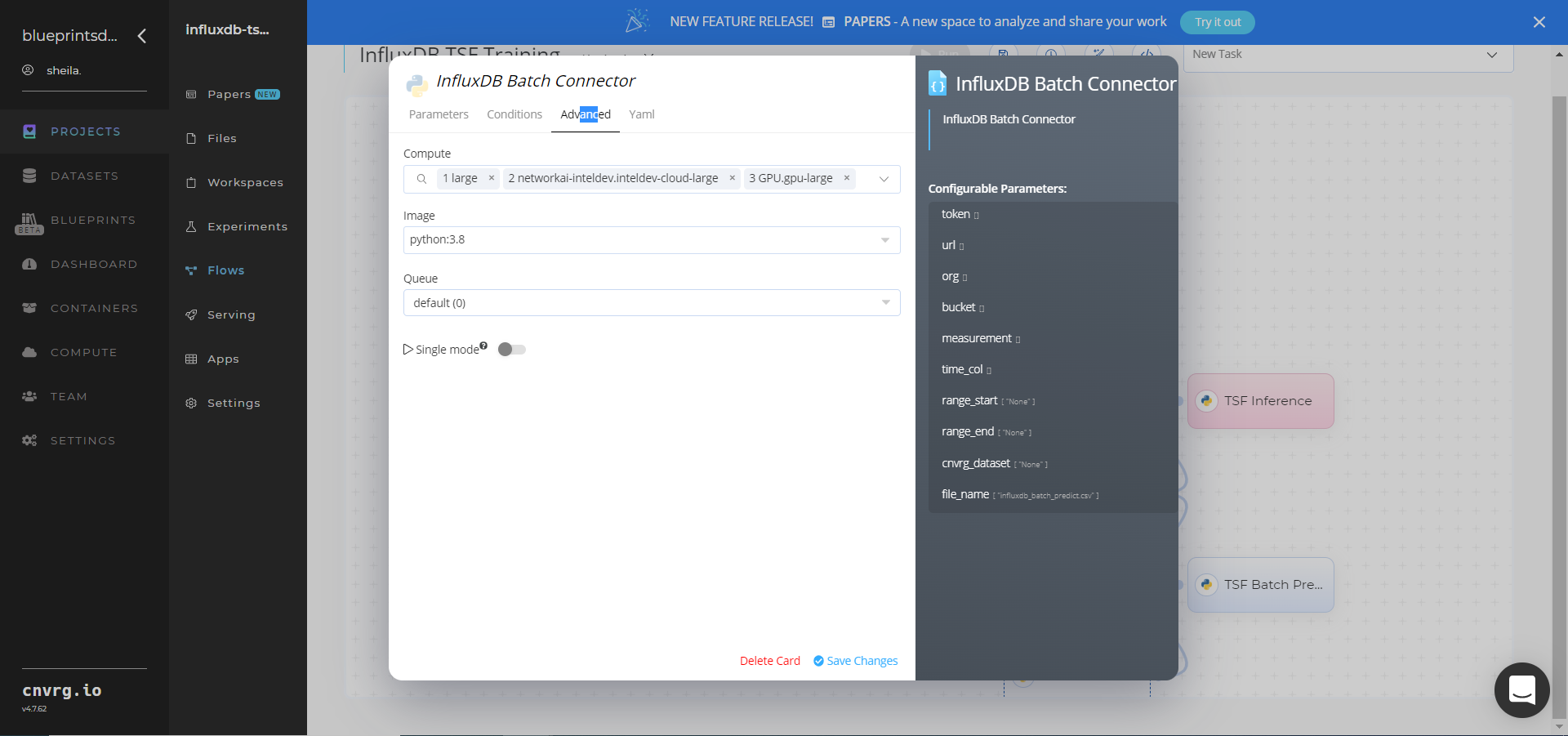
- Within the InfluxDB Batch Connector > Parameters tab, set the following Key-Value pair information:
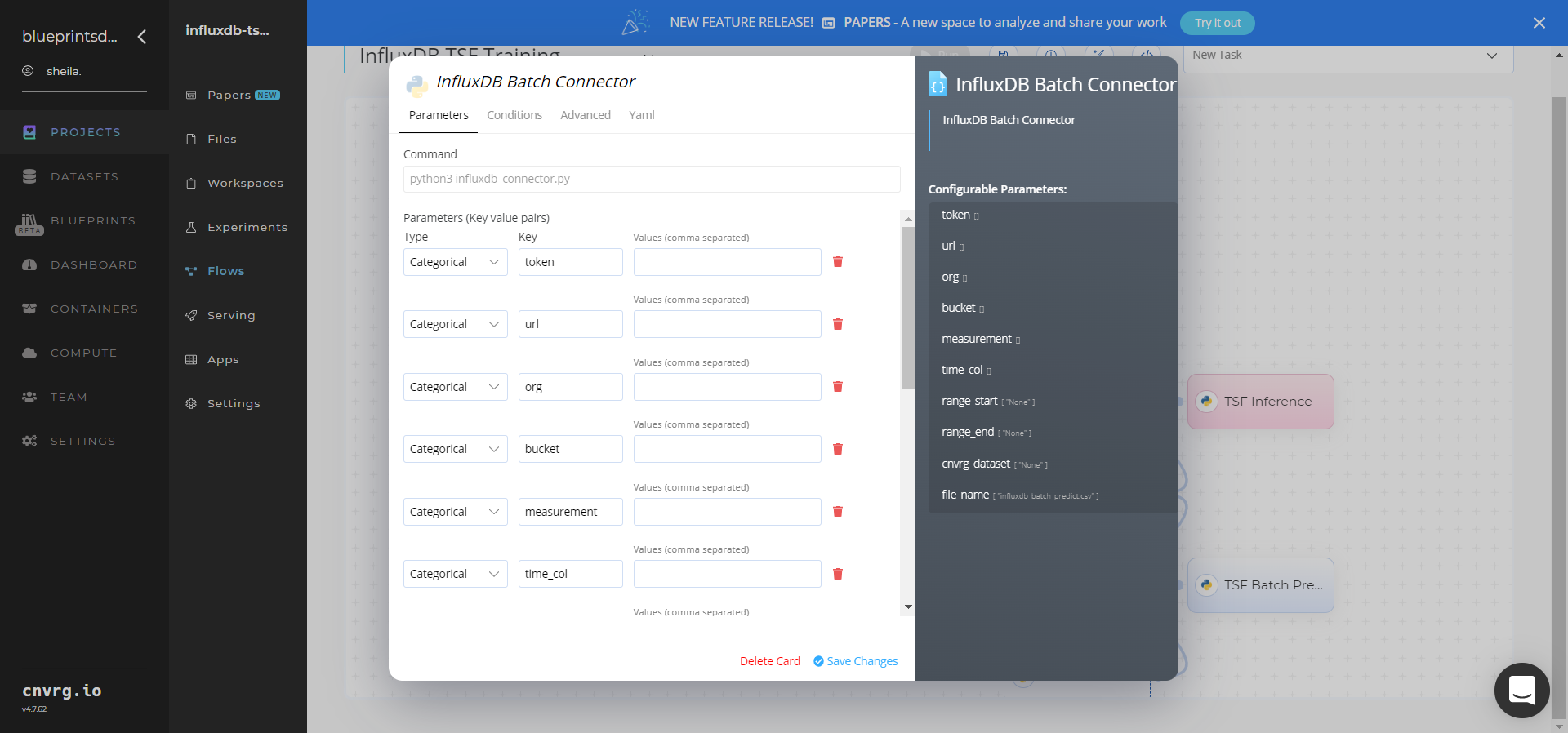
- Key:
token– Value: provide the InfluxDB API token - Key:
url– Value: provide the InfluxDB URL - Key:
org– Value: provide the organization email - Key:
bucket– Value: provide the data bucket name - Key:
measurement– Value: provide the measurement from which to pull data - Key:
time_col– Value: provide the name of the time column - Key:
range_start– Value: specify the start date for pulling time-series data from InfluxDB - Key:
range_end– Value: specify the end date for pulling time-series data from InfluxDB - Key:
cnvrg_dataset– Value: set to store the time-series data as a cnvrg dataset - Key:
file_name– Value: name the output CSV file
- Key:
- Click the InfluxDB Batch > Advanced tab to change resources to run the blueprint, as required.
- Within the S3 Batch Connector > Parameters tab, set the following Key-Value pair information:
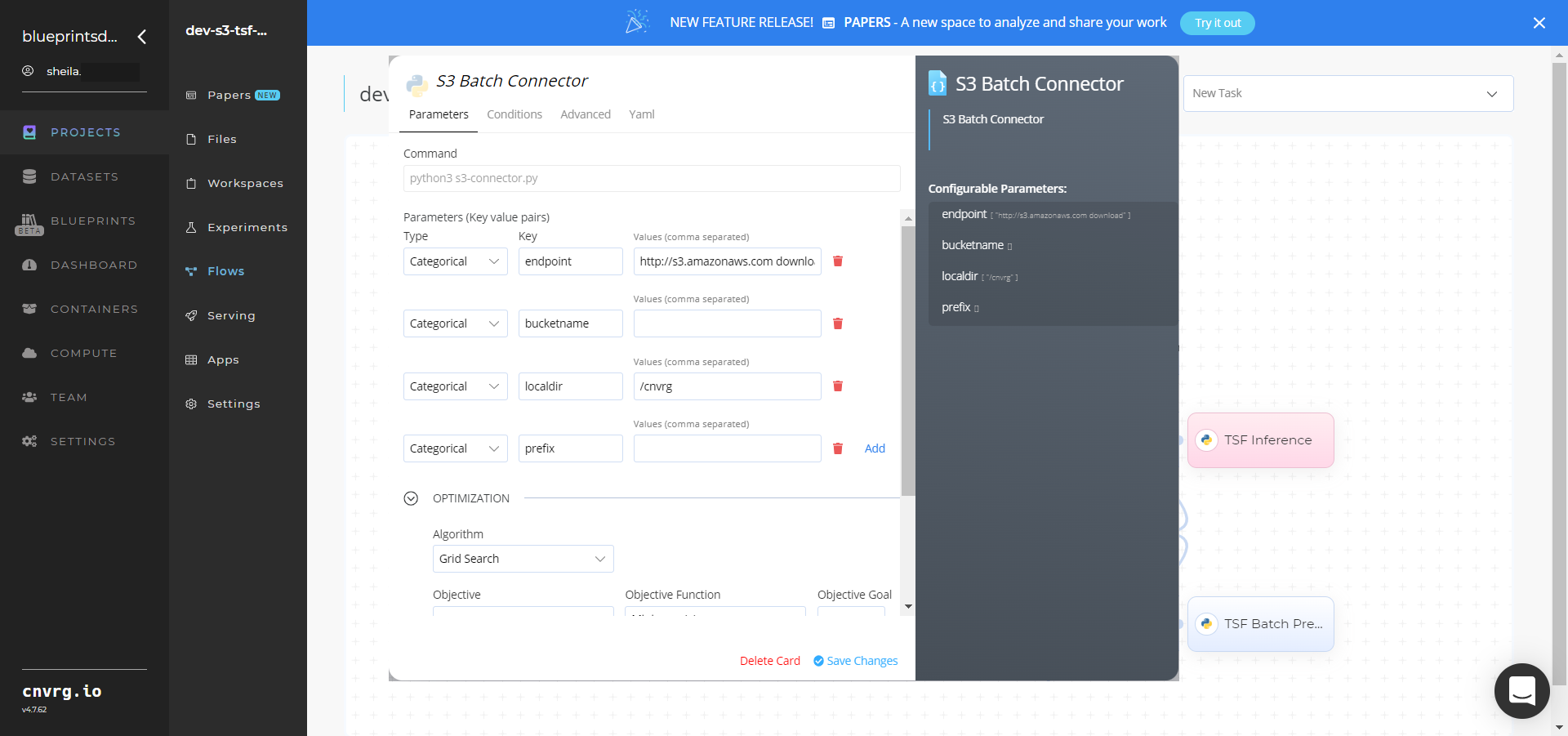
- Key:
bucketname– Value: provide the bucket name - Key:
prefix− Value: provide the main path to the data folder
- Key:
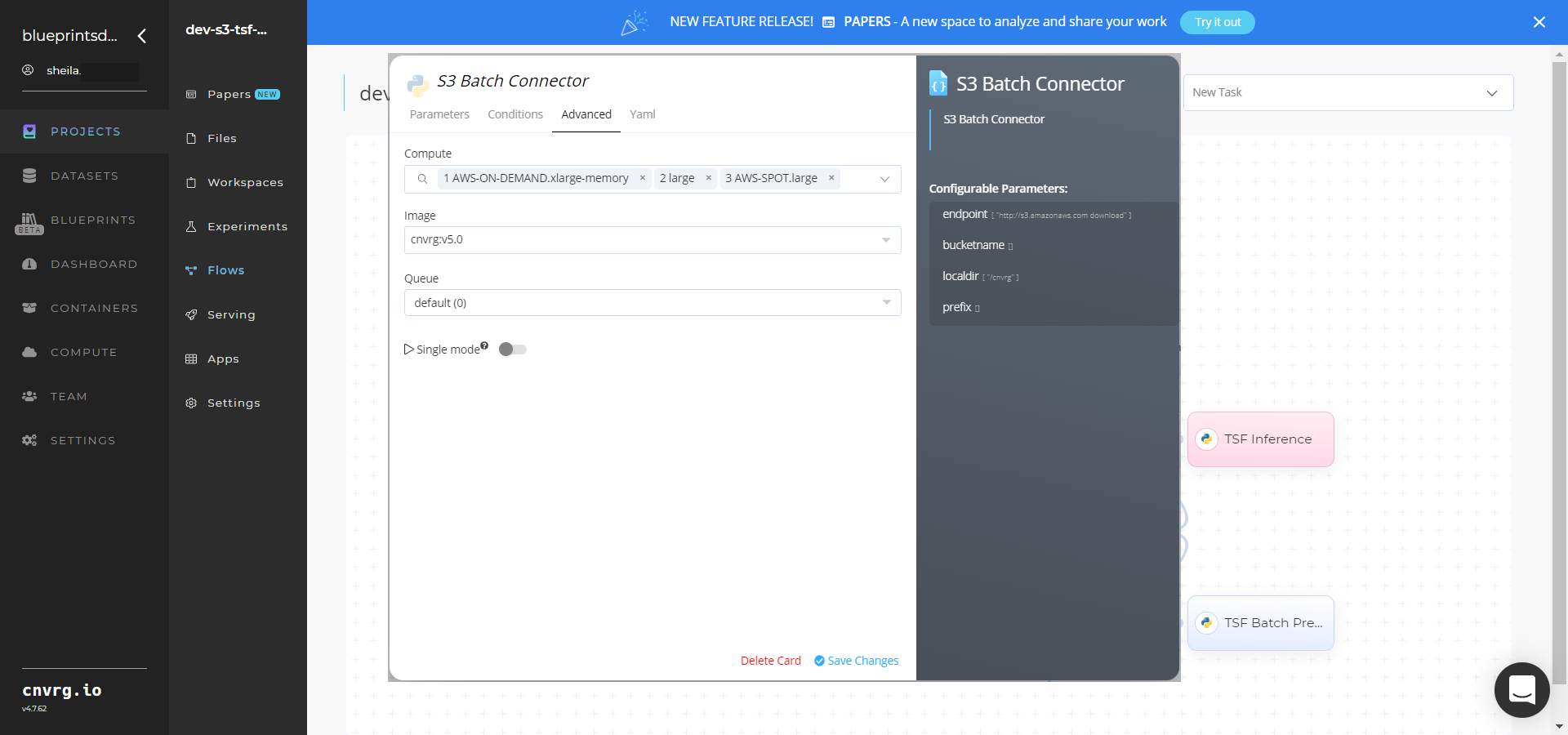
- Click the S3 Batch Connector > Advanced tab to change resources to run the blueprint, as required.
- Within the InfluxDB Batch Connector > Parameters tab, set the following Key-Value pair information:
Click the Run button.
 The cnvrg software launches the training blueprint as set of multiple experiments, selecting the best sensor-predictor algorithm and version for API deployment use based on a custom dataset.
The cnvrg software launches the training blueprint as set of multiple experiments, selecting the best sensor-predictor algorithm and version for API deployment use based on a custom dataset.NOTE
The time required for model training and endpoint deployment depends on the size of the training data, the compute resources, and the training parameters.
For more information on cnvrg endpoint deployment capability, see cnvrg Serving.
Track the blueprint’s real-time progress in its Experiments page, which displays artifacts such as logs, metrics, hyperparameters, and algorithms.
Click the Serving tab in the project and locate your endpoint.
Complete one or both of the following options:
- Use the Try it Live section with any data to check your model.

- Use the bottom integration panel to integrate your API with your code by copying in the code snippet.

- Use the Try it Live section with any data to check your model.
A custom model and API endpoint, which can forecast sensor-data values, have now been trained and deployed. For these blueprints’ software versions and release details, see InfluxDB TSF Train and S3 TSF Train.
# Connected Libraries
Refer to the following libraries connected to this blueprint:
- InfluxDB Connector
- S3 Connector
- TSF-Preprocess library
- TSF-Split data library
- TSF-ARMA model
- TSF-ARIMA model
- TSF-SARIMA model
- TSF-Compare library
- TSF-Inference library
- TSF-Batch Predict library
# Related Blueprints
Refer to the following blueprints related to this training blueprint: