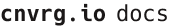# Run Hyperparameter tuning using Ray
cnvrg.io provides an easy way to run hyperparameter tuning using ray and cnvrg

# Create a Ray Cluster
In order to run a ray cluster, you need to first create a ray cluster:
- Go to the Compute page in the organization menu
- Click on Add new template
- In the templates page choose type "Ray"
- Fill in Master & Workers specifications and save it
# Add a ray Container
We will want to use an existing ray container, so the ray dependencies will be prebuilt:
- Go to the Containers page in the organization menu
- Click on Add new Image and choose -- "Pull Image":
- In the Registry choose "Docker Hub"
- In the Repository set: rayproject/ray
- In the tag set: latest
- Save the new Image
# Add the cnvrg callback to your project
Save the following code as a file in your project - cnvrgcallbak.py
from ray.tune.logger import LoggerCallback
from cnvrg import Experiment as CNVRGExperiment
class CNVRGCallback(LoggerCallback):
def __init__(self, tracked_metrics=None):
self._cnvrg_metrics = tracked_metrics if tracked_metrics else []
self._cnvrg_experiments = {}
super(LoggerCallback, self).__init__()
def log_trial_start(self, trial):
e = CNVRGExperiment.init()
self._cnvrg_experiments[trial.trial_id] = e['slug']
config = trial.config.copy()
config.pop("callbacks", None)
e.log_param("trial_id", trial.trial_id)
e.log_param("run_id",trial.trial_id.split("_")[0])
e.log(str(config))
for item in config:
e.log_param(item, config.get(item))
e.log( "======")
e.log(str(trial))
def log_trial_result(self, iteration, trial, result):
e = CNVRGExperiment(self._cnvrg_experiments[trial.trial_id])
e.log(str(result))
if self._cnvrg_metrics == []:
self._cnvrg_metrics = [key for key in result]
training_iteration = result['training_iteration']
for key in self._cnvrg_metrics:
try:
value = float(result[key])
except (ValueError, TypeError):
continue
e.log_metric(key, value, training_iteration)
def log_trial_end(self, trial, failed):
e = CNVRGExperiment(self._cnvrg_experiments[trial.trial_id])
e.log("===== Logging Artifacts =====")
from os import listdir
files_list= [os.path.join(trial.logdir, p) for p in os.listdir(trial.logdir)]
e.log_artifacts(files_list)
e.finish(exit_status=int(failed))
# Launch ray cluster
In order to run experiments on the ray cluster, execute:
import ray
ray.init(address="localhost:6379")
# Use cnvrg callback in ray tune function
When you want to run your code using run ray.tune you need to import the cnvrg callback:
from cnvrgcallbak import CNVRGCallback
and in the tune function add the CNVRGCallback:
tracked_metrics = ['mean_accuracy']
analysis = tune.run(
train_mnist,
metric="mean_accuracy",
local_dir=".",
mode="max",
name="exp",
scheduler=sched,
stop={
"mean_accuracy": 0.98,
"training_iteration": 5
},
callbacks=[CNVRGCallback(tracked_metrics)],
num_samples=5,
config={
"lr": tune.loguniform(1e-4, 1e-2),
"momentum": tune.uniform(0.1, 0.9),
})
# Ray Dashboard
You can use the ray dashboard to track the cluster and executions - by clicking on the ray icon in the workspace or in the experiment menu
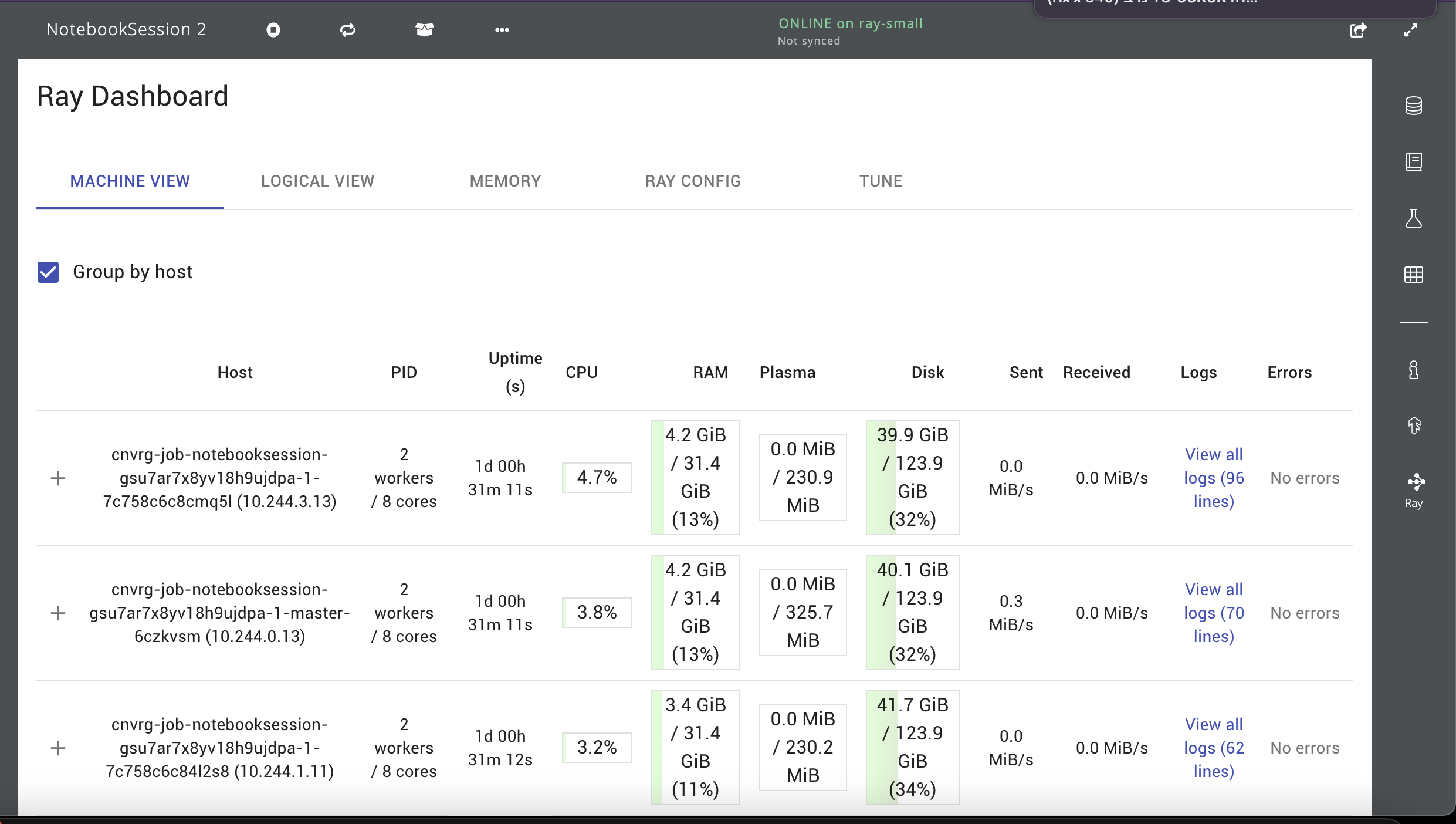
# Track & View experiments
Every experiment will be executed on the ray cluster. Every experiment will have a tag run_id
and you can track all the experiments by using the run_id. Each experiment will also have trial_id
to identify a specific trial_id